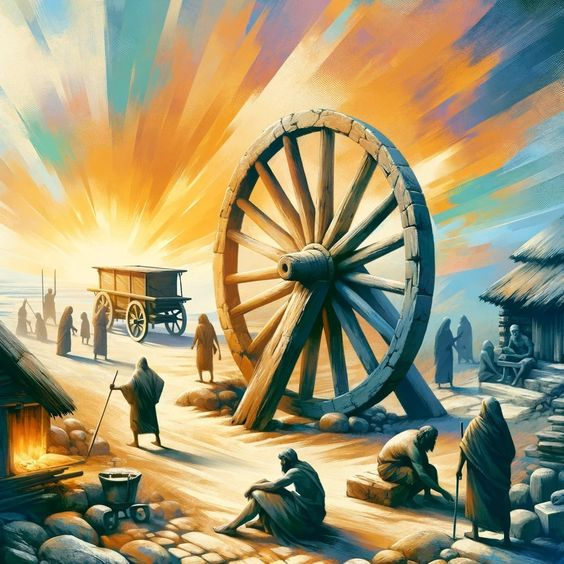
When Was the Wheel Invented
The wheel is one of humanity’s most significant inventions, revolutionizing transportation, industry, and daily life. Its development marked a pivotal moment in technological advancement. This article explores the history of the wheel, its invention, and its impact on civilization.
The Invention of the Wheel
1. Early Beginnings
The invention of the wheel is a milestone in human history that dates back to ancient times. However, it’s important to note that the wheel as we understand it today evolved over several centuries, with various stages of development. Don’t Miss to Check Out Our Website: healthybliss.xyz
2. The Earliest Evidence
a. The First Wheel:
- Date: The earliest known wheel dates back to around 3500 BCE.
- Location: The wheel was invented in Mesopotamia, in the region that is now modern-day Iraq.
b. The Uruk Period:
- Historical Context: The wheel first appeared during the Uruk period, a time of significant technological and cultural development in Mesopotamia. Archaeological evidence suggests that wheels were initially used for pottery making rather than transportation.
3. The Development of the Wheel for Transportation
a. The Chariot Wheel:
- Date: By around 2000 BCE, the wheel was adapted for use in transportation, notably in the construction of chariots.
- Location: The use of the wheel in chariots spread from Mesopotamia to various regions, including the Indus Valley, Egypt, and Europe.
b. Innovations:
- Spoked Wheels: Around 1500 BCE, spoked wheels were developed, enhancing the wheel’s efficiency and reducing its weight. This innovation significantly improved the performance of wheeled vehicles, such as chariots and carts.
Impact and Significance
1. Technological Advancements
a. Transportation:
- The wheel revolutionized transportation, making it possible to move goods and people more efficiently. It played a crucial role in the development of trade routes and the expansion of civilizations.
b. Industry:
- Beyond transportation, the wheel was instrumental in various industrial applications, including water mills and windmills, which facilitated agricultural and mechanical advancements.
2. Cultural and Societal Implications
a. Trade and Expansion:
- The wheel enabled the growth of trade networks by making it easier to transport goods over long distances. This facilitated cultural exchange and the spread of ideas between different regions.
b. Urbanization:
- The wheel contributed to the development of cities and urban centers by improving the movement of materials and resources, leading to more complex and organized societies.
Evolution and Modern Applications
1. Evolution of Wheel Design
a. The Industrial Revolution:
- During the Industrial Revolution, wheel technology continued to evolve, with improvements in materials and manufacturing techniques. This period saw the development of wheels for various applications, including railways and automobiles.
b. Contemporary Wheels:
- Modern wheels are designed using advanced materials, such as alloys and synthetic polymers, and are used in a wide range of vehicles, from bicycles to spacecraft.
2. Innovative Uses
a. Robotics:
- In robotics, wheels are used for mobility, enabling robots to navigate various environments. Advances in wheel design contribute to the efficiency and functionality of robotic systems.
b. Space Exploration:
- Wheels are also crucial in space exploration, where they are used in rovers and other equipment designed to explore the surface of other planets and moons.
Conclusion
The invention of the wheel is a landmark event in human history, marking the beginning of numerous technological advancements that have shaped our world. From its early use in pottery to its role in transportation, industry, and modern applications, the wheel has had a profound and lasting impact on civilization. Understanding its origins and evolution provides insight into the development of technology and its influence on society throughout the ages.
FAQs
Q1: Who invented the wheel?
A1: The invention of the wheel is attributed to the people of ancient Mesopotamia around 3500 BCE. It was initially used for pottery making before being adapted for transportation.
Q2: What was the wheel used for initially?
A2: The earliest wheels were used for pottery making. It wasn’t until around 2000 BCE that wheels were adapted for use in transportation, such as chariots and carts.
Q3: When did spoked wheels become common?
A3: Spoked wheels, which were lighter and more efficient, became common around 1500 BCE. This innovation significantly improved the performance of wheeled vehicles.
Q4: How did the wheel impact ancient civilizations?
A4: The wheel had a profound impact on ancient civilizations by revolutionizing transportation, facilitating trade, and contributing to the growth of cities and complex societies.
Q5: What are some modern applications of the wheel?
A5: Modern applications of the wheel include vehicles such as cars and bicycles, robotics, and space exploration equipment. Advances in wheel design continue to play a crucial role in various technological fields.

Daniel Lee, a versatile writer whose passion for storytelling shines through his insightful articles. Daniel’s writing spans a diverse range of topics, from technology and business trends to culture, education, and beyond. With a blend of meticulous research and engaging prose, Daniel captivates readers by unraveling complex subjects with clarity and depth. His articles not only inform but also inspire, encouraging readers to explore new ideas and perspectives. Whether diving into the latest innovations or examining timeless societal issues, Daniel’s words provoke thought and invite readers to broaden their understanding of the world around them.